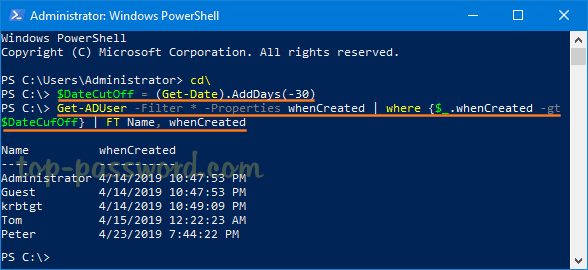
As a system administrator, you may find it’s difficult to keep track of BitLocker recovery keys for all computers in company network, especially when number of machines is more than 100. In this tutorial we’ll show you how to set the group policy to automatically backup BitLocker recovery information to Active Directory, so you can centrally manage the recovery keys/passwords in one place.
How to Configure GPO to Automatically Save BitLocker Recovery Key to AD
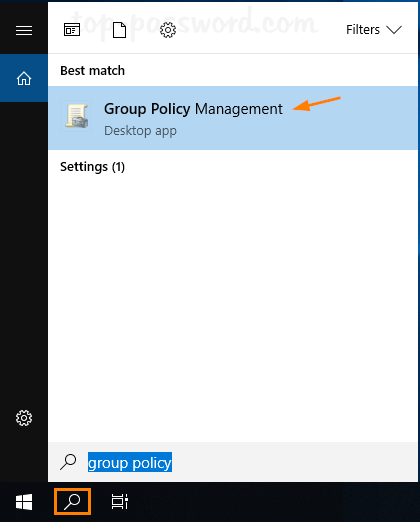
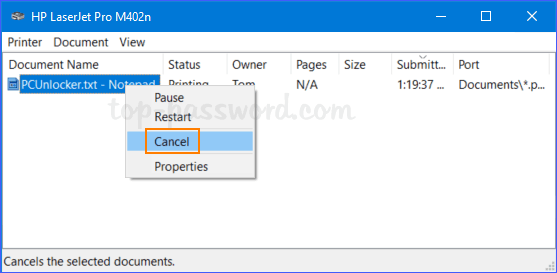
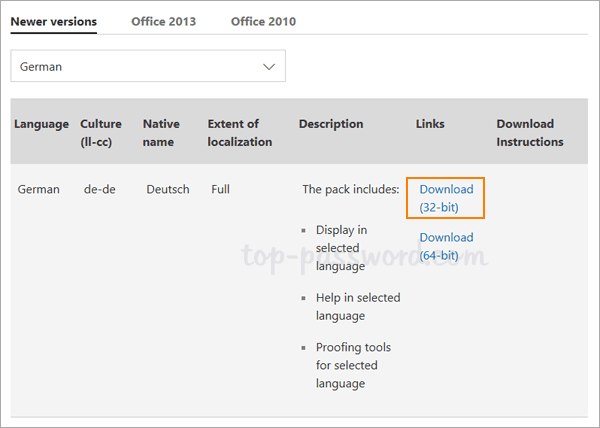
- Click the Search icon in the taskbar and type “group policy“. You can then click Group Policy Management to launch it.
![]()
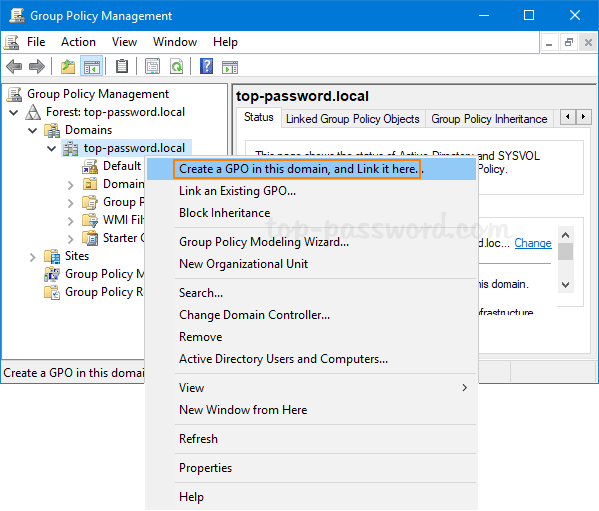
- Now in the left pane of Group Policy Management, right-click your AD domain and select “Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…” from the menu.
![]()
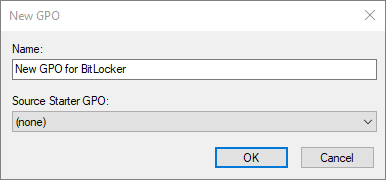
- In the New GPO dialog, give the GPO a name and click OK.
![]()
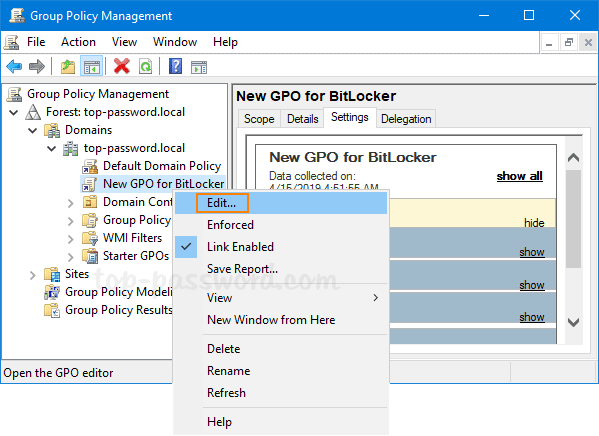
- Right-click the newly-created GPO in the left pane, and select Edit.
![]()
- Browse to
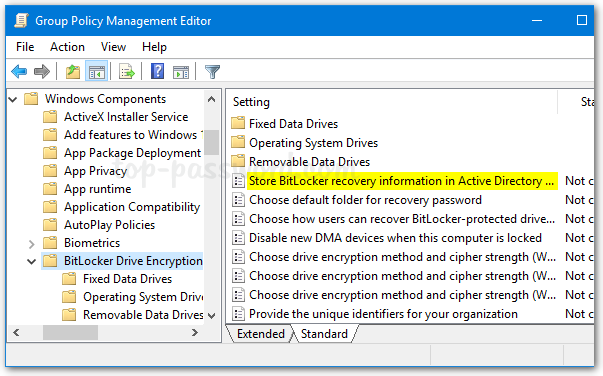
Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> BitLocker Drive Encryption, and then double-click the policy “Store BitLocker recovery information in Active Directory Domain Services“.![]()
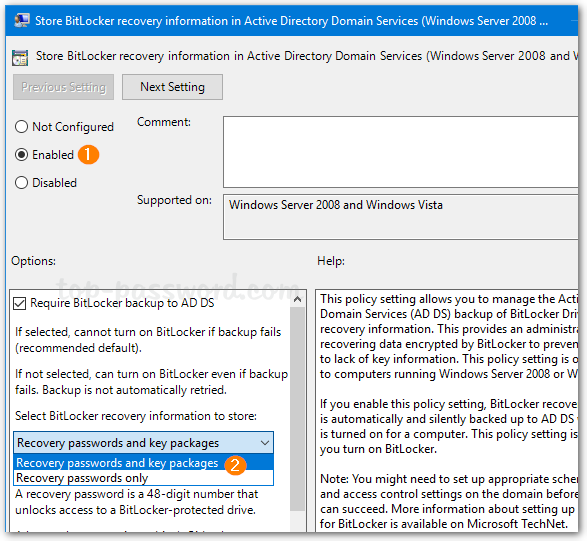
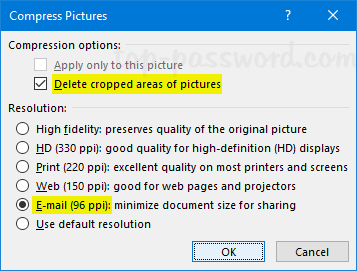
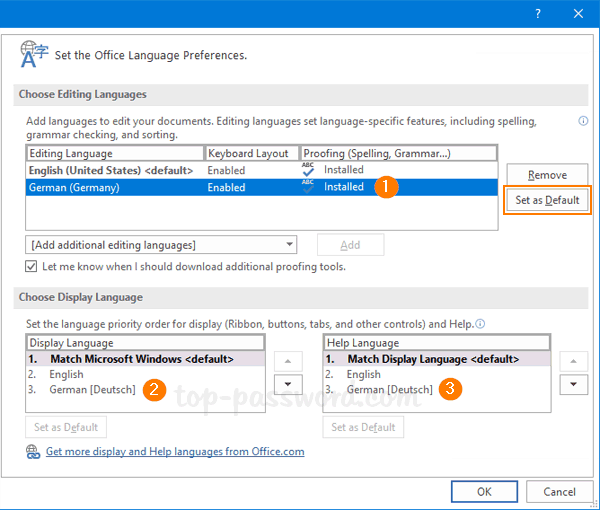
- Set the policy to Enabled. Make sure the “Require BitLocker backup to AD DS” option is checked, and select to store both recovery passwords and key packages.
![]()
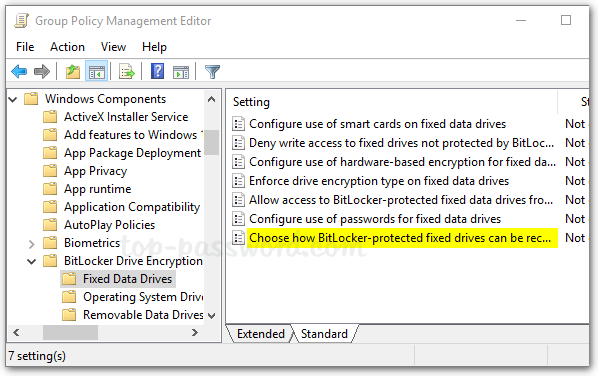
- Next, expand BitLocker Drive Encryption in the left pane. You’ll see three nodes: Fixed Data Drives, Operating System Drives, Removable Data Drives. Just select Fixed Data Drives and double-click the policy “Choose how BitLocker-protected fixed drives can be recovered“.
![]()
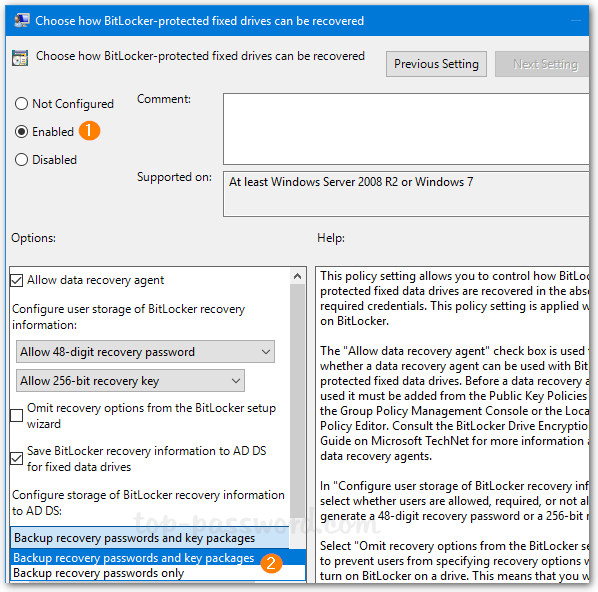
- Set it to Enabled. Check the options “Save BitLocker recovery information to AD DS for fixed drives” and then click OK.
![]()
- Go to the “Operating System Drives” node and turn on the similar policy “Choose how BitLocker-protected operating system drives can be recovered“. Afterwards, go to the “Removable Data Drives” node and enable the policy “Choose how BitLocker-protected removable drives can be recovered“.
- When any client PC retrieves the policy changes, BitLocker recovery information will be automatically and silently backed up to AD DS when BitLocker is turned on for fixed drives, OS drives or removable drives.
Manually Backup BitLocker Password to AD with PowerShell
If you have enabled BitLocker prior to configuring the above GPO policy, you can use PowerShell cmdlets to manually upload the BitLocker recovery key to Active Directory. Follow these steps:
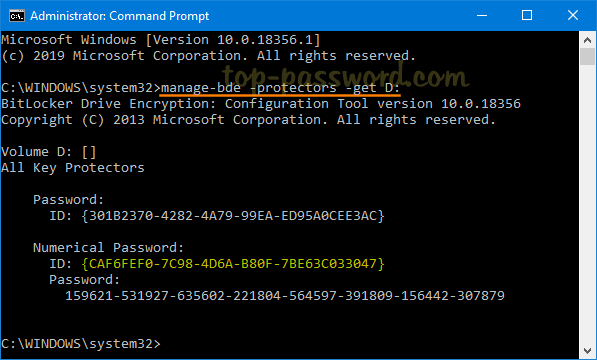
- When your BitLocker-protected drive is unlocked, open PowerShell as administrator and type this command:
manage-bde -protectors -get D:![]()
What you need to take note of is the Numerical Password ID.
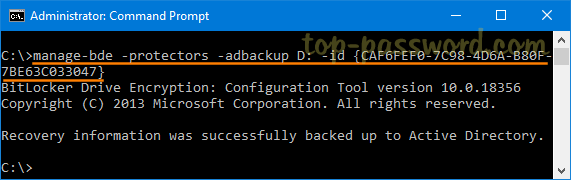
- Next, type the following command to backup your BitLocker recovery password to Active Directory. Remember you have to use the Numerical Password ID obtained on the previous step.
manage-bde -protectors -adbackup D: -id {CAF6FEF0-7C98-4D6A-B80F-7BE63C033047}![]()
- When that completes, you will receive the message “Recovery information was successfully backed up to Active Directory.“